Processor - Appleseed
Contents
Step 1. (Oil In)
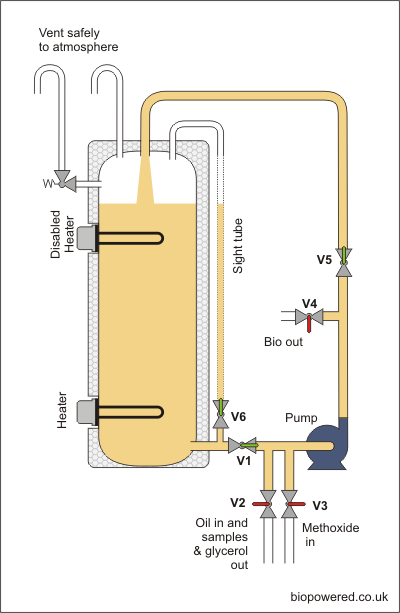
As this design of processor has no de-watering facility, it is important to ensure you oil is free of water to reduce the likelihood of soap formation. This can be done in a separate tank see step 3 of Processor - basic design, or a Glycerol wash may help. Unless your processor pump is self priming, or you store your oil in an adjacent tank whose level is higher than your pump you may have difficulty priming the pump to fill the reactor. An alternative method is to use a separate, self priming, pump such as a hand operated barrel pump. Open V1, V6 and V7, connect your oil supply, open V2 and either run the processor pump or operate the hand pump. Fill to a predetermined level marked on the sight glass. This level should be roughly 75% of the tanks capacity, allowing for the addition of 20% Methoxide and a small ullage space.
Step 2. (Heat Oil)
Double check that your reactor is filled with the correct amount of oil and close valve V2. Close valve V7 for safety and because with this design of sight tube and valve arrangement, un-reacted oil will be trapped within the tube. Open valves V1 and V5, with the pump running, to re-circulate oil around the tank and switch on the heater, only if you are certain the tank is filled to 75% and that the pump is running. Heat the oil to around 55°C It is dangerous to add heat if the level is too low, because you may expose the heating element, which would then overheat and ignite the oil in the tank. You could have a tank explosion. You must run the pump whenever the heater is on, so that there is a steady flow of oil to cool the element. While the oil is heating titrate your oil and mix your Methoxide. Once process temperature is reached turn off the heater.
Step 3. (Add the Methoxide)
With valves V1, V5 and V6 open, connect the methoxide tank to V3 and ensuring the tank is vented to a safe area. Check that the heater is switched off and switch on the pump. Gradually open V3 to allow the suction of the pump to draw methoxide out of the tank. A preferred method of introducing Methoxide is to use a venturi As the Methoxide is introduced very close to the pump, it is preferable to introduce it gradually and slowly, so the bulk of the flow through the pump is oil. Unless you have splashed out on a pump specifically designed to pump flammable chemicals such as Methanol, it is far safer to spend a little time introducing the Methoxide than run the risk of high concentrations of Methoxide passing through the pump. When the dosing is complete, shut off valves V3 and V6.
Step 6. (The reaction stage)
Valves V1 and V5 should be fully open. Check that V6 and V7 are closed, and that the heater is off. Allow the pump to run for around 90 to 120 minutes, which should be long enough for your reaction to reach its peak of conversion from oil to biodiesel. Your temperature should remain at around 50-55°C throughout the reaction. After the reaction period has elapsed, switch off the pump.
Step 7. (Settle the glycerol)
Glycerol is denser than biodiesel so will drop to the bottom of the reaction vessel, carrying with them most of the soap which is formed as a by product, and any unused catalyst. Allow 90 minutes or more for this settling to happen. Be aware that if you leave the processor too long, say more than a few hours, the settled glycerol in the pipe work may form a thick gel if you are using NaOH as a catalyst and especially in cold weather. This can block your pipe work and jam the pump.
Step 8. (Drain the glycerol)
Open valve V6 and attach your glycerol collection container to valve V2. It is preferable that this container is sealed and has a vent to a safe area. If it hasn’t, take great care to perform this operation in a well ventilated space and not to inhale any vapours being displaced from the container. Now open valve V3 slightly to allow a slow trickle of glycerol to run into the collection container. You can expect to collect up to 25% of the volume of the oil you used, as glycerol so you should ensure that you container is of sufficient volume. You will see when all the glycerol has been drained, because the drained liquid will suddenly become much lighter in colour and runnier as the flow changes to biodiesel. Close V3 completely now and wait a couple of minutes. Re-open V3 very slightly and you should be able to drain off a little more glycerol. When no more glycerol flows, close V3 and remove and seal the Glycerol collection container.
Step 9. (Drain the biodiesel)
You can now pump out the Biodiesel for further treatment, either bubbling and settling or water washing. Double check that the heater is switched off (remember an exposed, live heater will glow red hot and will, more than likely, cause an explosion). With valve V7 still closed retaining the un-reacted oil in the sight tube, open valves V1 and V6. Connect vale V4 to your bubbling or wash tank using pipe work or hose that is suitable for the temperature involved (around 55°C).
Open valve V4 and start the pump. If pumping into an open topped vessel, do so in a well ventilated space and avoid breathing any fumes evolved. The Biodiesel will still contain a percentage of Methanol and as the temperature is close to the boiling point, Methanol fumes will be evolved. Where possible it is preferable to decant into a closed and vented vessel.
Step 10. (Drain the sight tube)
Now the processor is empty the oil retained in the sight tube can be drained by placing a small container under valve V2 and opening valves V7 and V2. This oil can be returned to your oil storage.