Difference between revisions of "Still head heat exchanger"
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
File:SHHE photo3 source Mark.jpg|Completed SHHE. Source: mark | File:SHHE photo3 source Mark.jpg|Completed SHHE. Source: mark | ||
File:SHHE photo2 source Mark.jpg|Finished assembly. SHHE and [[Plumbers delight condenser]] (both multi core) Source: mark | File:SHHE photo2 source Mark.jpg|Finished assembly. SHHE and [[Plumbers delight condenser]] (both multi core) Source: mark | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery caption="SHHE using a commercially made heat exchanger." widths="250px" heights="300px" perrow="3" align="center"> | ||
| + | File:SHHE3 julian.JPG|Commercially made, multi tube heat exchanger used as a SHHE. | ||
| + | File:SHHE1 julian.JPG|Heat exchanger before fitting. | ||
| + | File:SHHE2 julian.JPG|Internal view of the same heat exchanger. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 3 June 2011
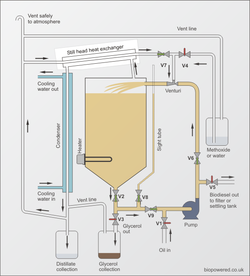
Still head heat exchanger (SHHE) is often used on biodiesel reactors to improve the efficiency of the condenser. SHHE are used with reactor designs that employ methanol recovery.
Contents
Benefits
- Reduces De-meth Times
- Reduces Power consumption of the immersion heater
- Reduces the heat transferred to the cooling water
Description
The still head heat exchanger is a vapour to air heat exchanger, transferring heat from water or methanol vapour exiting the reactor to air returning from the condenser to the reactor.
Placement
Placement of the heat exchanger needs to be done so that any condensed vapour can drain into the collection vessel. Often on the GL Eco reactor design SHHE are placed above the condenser to aid draining also being close to the return path of vapour from the condenser to the venturi
Examples
Often heat exchangers from domestic boilers are used, these have a large surface area which improves heat transfer.
- Multi core SHHE by mark
Finished assembly. SHHE and Plumbers delight condenser (both multi core) Source: mark
- SHHE using a commercially made heat exchanger.