Difference between revisions of "Biodiesel process guide"
(→Process overview) |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This is a fast | + | <metadesc>A quick guide to the biodiesel production process</metadesc> |
| + | This is a fast guide to the steps involved in making biodiesel according to the simplest process. | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| − | ==Dewatering== | + | ==Process overview== |
| − | # | + | |
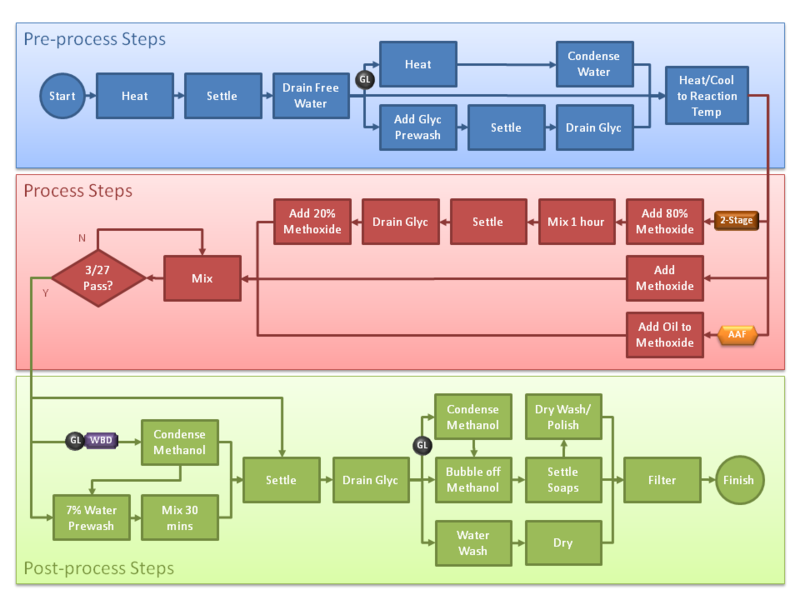
| − | # | + | This diagram shows the popular methods employed by brewers to produce biodiesel from used vegetable oil. Which parts of the process are followed come down to personal choice. The simplest path is detailed on this page. |
| − | # Take a sample for titration | + | |
| + | [[File:Process_flowchart_01.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pre-process== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Dewatering=== | ||
| + | # Raise oil temp to at least 60°C and allow to stand for at least one hour, over night is better | ||
| + | # Drop a few litres from the bottom, taking away any water that has settled | ||
| + | # Take a sample for titration | ||
# If necessary, transfer the oil to your processor | # If necessary, transfer the oil to your processor | ||
| − | ==Titration== | + | ==Process== |
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Titration]]=== | ||
# Add 10ml of IPA to a beaker | # Add 10ml of IPA to a beaker | ||
| − | # Add a few drops of | + | # Add a few drops of phenolphthalein or tumeric indicator solution |
| − | # With a syringe draw a little of your [[Titration#Reference_solution|titration solution]], and add dropwise to your beaker until your solution turns purple and stays purple for | + | # With a syringe draw a little of your [[Titration#Reference_solution|titration solution]], and add dropwise to your beaker until your solution turns purple and stays purple for approximately 30 seconds. This is known as blanking, to get the IPA to neutral pH. |
| − | # Add 1ml of | + | # Add 1ml of the oil sample drawn after dewatering and swirl - the solution will turn a yellow/white |
| − | # Fill a | + | # Fill a 1ml syringe with your [[Titration#Reference_solution|titration solution]] and add drop wise to your beaker, swirling constantly. You are trying to find the point where the solution goes and stays purple for 30 seconds. |
| − | # Work out the amount of titrant you have used. | + | # Work out the amount of titrant you have used. 1.4ml of titration solution = titration value of 1.4. Repeat this step if necessary to get an accurate value. |
| − | # Add | + | # Heat your oil to 55°C and turn off heater (make sure your pump is on and circulating) |
| − | # | + | |
| − | # | + | ===Mix [[methoxide]]=== |
| + | # Add the titration figure to your base. Most [[sodium hydroxide]] users use a base of 5.0g/l. In this example, 1.4 + 5.0 = 6.4g/l. This figure is the amount of sodium hydroxide needed '''per litre of oil you are going to process''' ([[potassium hydroxide]] users use a base of 7.0g/l, 1.4 + 7.0 = 8.4g/l) | ||
| + | # Measure out the sodium or potassium hydroxide | ||
| + | # Measure out the methanol (20% of the oil volume) | ||
| + | # Mix the methanol and sodium or potassium hydroxide to make methoxide | ||
| − | == | + | ===Mix methoxide and oil=== |
| − | # Inject methoxide via | + | # Inject methoxide via venturi or suck in via pump input |
# Process - allow to mix for one hour | # Process - allow to mix for one hour | ||
| − | # Take a sample for 3/27 or 5/45 and allow to sit for 10 minutes | + | # Take a sample for the 3/27 or 5/45 conversion test and allow to sit for 10 minutes |
| − | ===5/45 test=== | + | ===[[5/45 test]] (upscaled 3/27 test)=== |
# Add 45mls of methanol to a suitable container | # Add 45mls of methanol to a suitable container | ||
# Add 5mls of biodiesel from the top of your settled sample | # Add 5mls of biodiesel from the top of your settled sample | ||
| − | # Tightly close the lid and shake for 10-15 seconds (for accurate results your | + | # Tightly close the lid and shake for 10-15 seconds (for accurate results your methanol should be at 20°C) |
# Allow to stand for 5-10 minutes | # Allow to stand for 5-10 minutes | ||
| − | # Pass = solution | + | # Pass => transparent solution, fail => fall out/seperation of liquids (more mixing required) |
| + | |||
| + | ==Post-process== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Drain [[glycerol]]=== | ||
| + | # Turn off all pumps and settle for at least one hour. | ||
| + | # Drain glycerol slowly into suitable container - Glycerol is black and thick, when the lighter Biodiesel starts to flow out stop draining. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Finishing=== | ||
| + | Choose one of: | ||
| + | ====Finishing - [[Processor - with methanol condenser (GL design)|GL processors]]==== | ||
| + | # Condense excess methanol off from biodiesel | ||
| + | # Pump out to settle drum and stand, soaps to settle out naturally. This can take anything from a few hours to a few days depending on how well the biodiesel is demethed | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Finishing - Non-GL processors (waterless)==== | ||
| + | # Pump out to settle drum | ||
| + | # Air bubble biodiesel while still hot to drive off excess methanol - this should be done in a well ventilated environment | ||
| + | # Stand for soaps to settle out naturally. This can take anything from a few hours to a few days depending on how well the biodiesel is demethed | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Finishing - [[Water washing]]==== | ||
| + | # Water wash in processor or seperate water wash drum, which will remove both excess methanol and soap | ||
| + | # [[Drying_wet_biodiesel|Dry the wet biodiesel]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Soap tests]]== | ||
| + | # Fill a clean jam jar half full with a sample of your biodiesel and add the same amount of water | ||
| + | # Shake well, and allow to stand for approximately five minutes | ||
| + | # Pass => water at the bottom of your sample is clear, fail => creamy water | ||
| + | # Pass your fuel through at a 5 micron filter or smaller before putting into the car | ||
| − | == | + | ==See also== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * [[MSDS - Biodiesel ]] | |
| − | + | * [[MSDS - Glycerol ]] | |
| − | + | * [[MSDS - Methanol ]] | |
| + | * [[MSDS - Potassium Hydroxide ]] | ||
| + | * [[MSDS - Sodium Hydroxide ]] | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Biodiesel]] | [[Category:Biodiesel]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Processing methods]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:49, 22 July 2015
This is a fast guide to the steps involved in making biodiesel according to the simplest process.
Process overview
This diagram shows the popular methods employed by brewers to produce biodiesel from used vegetable oil. Which parts of the process are followed come down to personal choice. The simplest path is detailed on this page.
Pre-process
Dewatering
- Raise oil temp to at least 60°C and allow to stand for at least one hour, over night is better
- Drop a few litres from the bottom, taking away any water that has settled
- Take a sample for titration
- If necessary, transfer the oil to your processor
Process
Titration
- Add 10ml of IPA to a beaker
- Add a few drops of phenolphthalein or tumeric indicator solution
- With a syringe draw a little of your titration solution, and add dropwise to your beaker until your solution turns purple and stays purple for approximately 30 seconds. This is known as blanking, to get the IPA to neutral pH.
- Add 1ml of the oil sample drawn after dewatering and swirl - the solution will turn a yellow/white
- Fill a 1ml syringe with your titration solution and add drop wise to your beaker, swirling constantly. You are trying to find the point where the solution goes and stays purple for 30 seconds.
- Work out the amount of titrant you have used. 1.4ml of titration solution = titration value of 1.4. Repeat this step if necessary to get an accurate value.
- Heat your oil to 55°C and turn off heater (make sure your pump is on and circulating)
Mix methoxide
- Add the titration figure to your base. Most sodium hydroxide users use a base of 5.0g/l. In this example, 1.4 + 5.0 = 6.4g/l. This figure is the amount of sodium hydroxide needed per litre of oil you are going to process (potassium hydroxide users use a base of 7.0g/l, 1.4 + 7.0 = 8.4g/l)
- Measure out the sodium or potassium hydroxide
- Measure out the methanol (20% of the oil volume)
- Mix the methanol and sodium or potassium hydroxide to make methoxide
Mix methoxide and oil
- Inject methoxide via venturi or suck in via pump input
- Process - allow to mix for one hour
- Take a sample for the 3/27 or 5/45 conversion test and allow to sit for 10 minutes
5/45 test (upscaled 3/27 test)
- Add 45mls of methanol to a suitable container
- Add 5mls of biodiesel from the top of your settled sample
- Tightly close the lid and shake for 10-15 seconds (for accurate results your methanol should be at 20°C)
- Allow to stand for 5-10 minutes
- Pass => transparent solution, fail => fall out/seperation of liquids (more mixing required)
Post-process
Drain glycerol
- Turn off all pumps and settle for at least one hour.
- Drain glycerol slowly into suitable container - Glycerol is black and thick, when the lighter Biodiesel starts to flow out stop draining.
Finishing
Choose one of:
Finishing - GL processors
- Condense excess methanol off from biodiesel
- Pump out to settle drum and stand, soaps to settle out naturally. This can take anything from a few hours to a few days depending on how well the biodiesel is demethed
Finishing - Non-GL processors (waterless)
- Pump out to settle drum
- Air bubble biodiesel while still hot to drive off excess methanol - this should be done in a well ventilated environment
- Stand for soaps to settle out naturally. This can take anything from a few hours to a few days depending on how well the biodiesel is demethed
Finishing - Water washing
- Water wash in processor or seperate water wash drum, which will remove both excess methanol and soap
- Dry the wet biodiesel
Soap tests
- Fill a clean jam jar half full with a sample of your biodiesel and add the same amount of water
- Shake well, and allow to stand for approximately five minutes
- Pass => water at the bottom of your sample is clear, fail => creamy water
- Pass your fuel through at a 5 micron filter or smaller before putting into the car